Understanding the File Structure of React Native Project
Introduction:
This blog aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the file structure generated after creating a React Native project. To begin, let's explore how to create a React Native project using the following command:
npx @react-native-community/cli@latest init RNFirstProject
Here, RNFirstProject is the project name which we were creating and it is using react-native latest version.
Creating a Project with a Specific Version:
If you prefer to create a project with a specific React Native version, you can utilize the following command format:
npx @react-native-community/cli@X.XX.X init YourProjectName --version X.XX.X
Replace "YourProjectName" with your desired project name, and "X.XX.X" with the specific React Native version you wish to use.
Explanation: Upon executing the initialization command, React Native generates a standardized file structure.
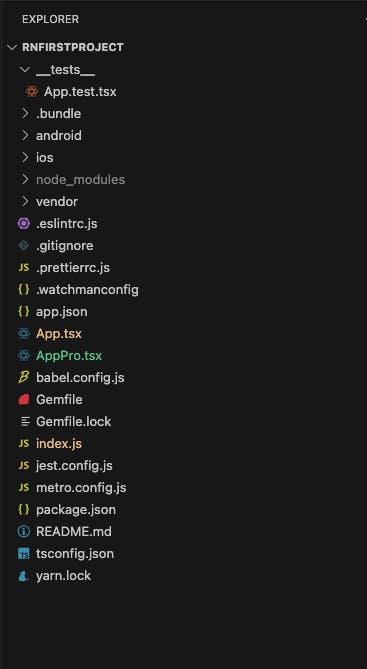
Breakdown of Key Directories and Files:
android/:
Contains all Android-specific code and resources.
The
build.gradlefile within android can be checked for dependencies, minimum SDK version, and target SDK version. Manual addition of dependencies may be required at times.
ios/:
Holds all iOS-specific code and resources.
Occasionally, the
Podfilein ios might need modifications, especially when adding new packages to the project.
node_modules/:
Houses all the project's dependencies.
In case of issues with
node_modules, deletenode_modulesthen try runningnpm installin the current working directory can recreate all node modules.
App.tsx:
- Where you begin building your React Native components.
index.js:
- The entry point of your application which is responsible for registering the root component of your application.
Additional Files:
.gitignore:
- Specifies patterns of files and directories that Git should ignore, preventing unnecessary files from being tracked by version control.
prettierc.js:
- Contains configuration options for Prettier, maintaining consistent code style across the project.
watchman:
- A tool developed by Facebook for watching file changes and triggering actions in response, aiding in efficient development with tools like Metro bundler.
app.json:
- Configures various aspects of a React Native application such as display name, bundle identifier, version number, and platform-specific configurations.
babel.config.js:
- Configures Babel, a JavaScript compiler, for transforming modern JavaScript code into backward-compatible versions. It is useful if you have multiple packages directories in your project that utilize a single babel config.
tsconfig.json:
- Contains TypeScript compiler options and settings if TypeScript is used in the React Native project.
package.json:
- A metadata file for a Node.js project, including dependencies, scripts for tasks, project details like name, version, and author information.
This arrangement provides a clearer separation between the key directories and files constituting the basic structure of a React Native project and the additional configuration and metadata files associated with it.